Potbelly ($PBPB) Analysis
Buy Recommendation
Investment Thesis:
Potbelly is within the framework of the American restaurant industry. The restaurant industry has seen healthy growth over the past few decades. The fast-food and the full-service sector have long been the two sectors that have dominated the industry. The rapidly growing fast-casual restaurants were able to squeeze themselves between the two and compete for market share. The fast-casual market share is 7.7% compared to the fast-food market share of 43.8% and 48.5% of the full-service sector.
With the previous management gone, Potbelly can improve its business through a proven franchise model. The company has hired several top former executives from Wendy’s and McDonald’s to lead the franchising and expansion efforts. Management can use customer loyalty and brand awareness to grow rapidly and start producing meaningful amounts of free cash flow.
Company Background:
Potbelly is a neighborhood sandwich concept offering toasty sandwiches, salads, and other menu items. The shops feature vintage design elements and locally-themed décor. Potbelly started in 1977 as a small antique store on Lincoln Avenue in Chicago. The original owner began offering sandwiches and desserts to customers to boost sales. As time passed, Potbelly became known as the sandwich shop in the neighborhood. The original owner sold the Lincoln Avenue store to Bryant Keil in 1996. Throughout the growth of Potbelly, each new shop has maintained a similar look and experience.
Competitive Positioning:
Potbelly has a high threat level of competition in the fast-casual industry. Chains such as Chipotle, Panera, Panda, Five Guys, and Wingstop have been the industry leaders and show no signs of slowing down. Intense competition within the fast-casual industry can drive down prices and decrease the company's overall profitability.
The fast-casual sector has a moderate level of threats from new entrants due to the high entry barriers of entry. The fixed capital cost to initially build a store is high, and significant government regulation surrounds food establishments and franchise licensing, further increasing the barriers. Potbelly has cleared a significant hurdle by establishing its current locations and receiving the necessary licenses. Competitors such as Chipotle, Panera, and Panda have long dominated the fast-casual with smaller competitors such as Potbelly's, Portillos, and Noodles. The company is working hard to get its sales and margins up. The threat of new entrants is moderate. The customer demand is changing; consumers are looking for quick, affordable, and slightly healthier meals than traditional fast food. New entrants in the fast-casual space can pressure Potbelly through innovation, lower pricing strategies, and provide unique value propositions to the customers. Potbelly must manage all these challenges and build practical barriers to safeguard its competitive edge. Potbelly can spend money on research and development. New entrants are less likely to enter a dynamic industry where established players such as Potbelly keep defining the standards regularly. This will help potbelly fight new entrants' threats and hold the potential danger of new threats at moderate to low.
Potbelly heavily relies on its suppliers to maintain its business. The power of suppliers for Potbelly is moderately high. They count on a limited number of suppliers for their significant products and have one distribution company for most of their national distribution program. Potbelly uses a third distributor known as Distribution Market Advantage (DMA) as a broker to negotiate on their behalf to gain access to third-party food distributors and suppliers. DMA has supplied Potbelly with 90-95% of its food supply. Potbelly depends heavily on very few suppliers, giving the supplier a great deal of power when determining prices. Almost all the bread purchased Is from Campagna-Turano Bakery and gets all its meat from a mix of nine suppliers. Potbelly works with suppliers to reduce the power of the supplier. They use a blend of forwarding pricing protocols for specific items, which are agreed on with the supplier on fixed prices for deliveries at some time in the future. The future formula pricing protocols under which Potbelly pays are based on a specified formula related to the prices of the goods, such as spot prices. Increased food prices and increased coemption and shortages can severely affect the supply of goods, ultimately impacting Potbelly's pricing and negatively affecting sales and profit margins. Potbelly must build an efficient supply chain with multiple suppliers. They can try experimenting with different products while maintaining quality by using various goods. If the prices go up for one material, the company can quickly shift to another.
Fast-casual restaurants are a type of quick-service restaurant (QSR). Compared with traditional fast food, fast-casual restaurants serve a higher quality of the food, their distinguishing factor. Panera Bread had sales of 5.9 billion and was the leading fast-casual restaurant in the United States in 2019. The growing demand for the sector is apparent, and as new entrants enter the market every year, the customers' bargaining power simultaneously goes up. The customer creates the demand and, in turn, can alter the price they want to pay due to all the options they have available to choose from. In the fast-casual sector, they are tons of options to choose from, and it is becoming increasingly difficult to differentiate yourself from the competitor. Potbelly must use a combination of technology implementation, great in-store experiences, fresh food, and reducing overhead costs, and renegotiating leases to differentiate and make more profits. The increased power of customers puts pressure on Potbelly to keep prices reasonable and consistently deliver a product that meets customers' expectations.
Power of customer is relatively low, Inflation of food vs potbelly prices- potbelly can pass inflation to customer. If the customer has power then they can’t up to their food by the same rate of inflation
Potbelly faces a high-level threat from substitute products and companies trying to compete for market share. Competitors in the specialized submarine sandwich such as Subway, Jimmy John, and substitutes like local delis or supermarket delis can take business from Potbelly if they begin to build new convenient locations or offer more enticing quality or prices. Potbelly must strategically choose where locations, whether that be for company-owned or franchises. A person's ability to switch from Potbelly to Subway or Jimmy Johns is relatively low; They can fight this high threat level by starting an effective loyalty program. Potbelly discussed in the third quarter of 2020 earnings calls that they have been making updates and additions to the loyalty program since the beginning of the year. They are continuing to add simplified programming and perks such as refer a friend and daily promotions. Potbelly has seen a 32% increase from Q3 of 2019 in perk-related purchases and has had a $1 million increase in perk-related purchasing on a quarter-over-quarter basis.
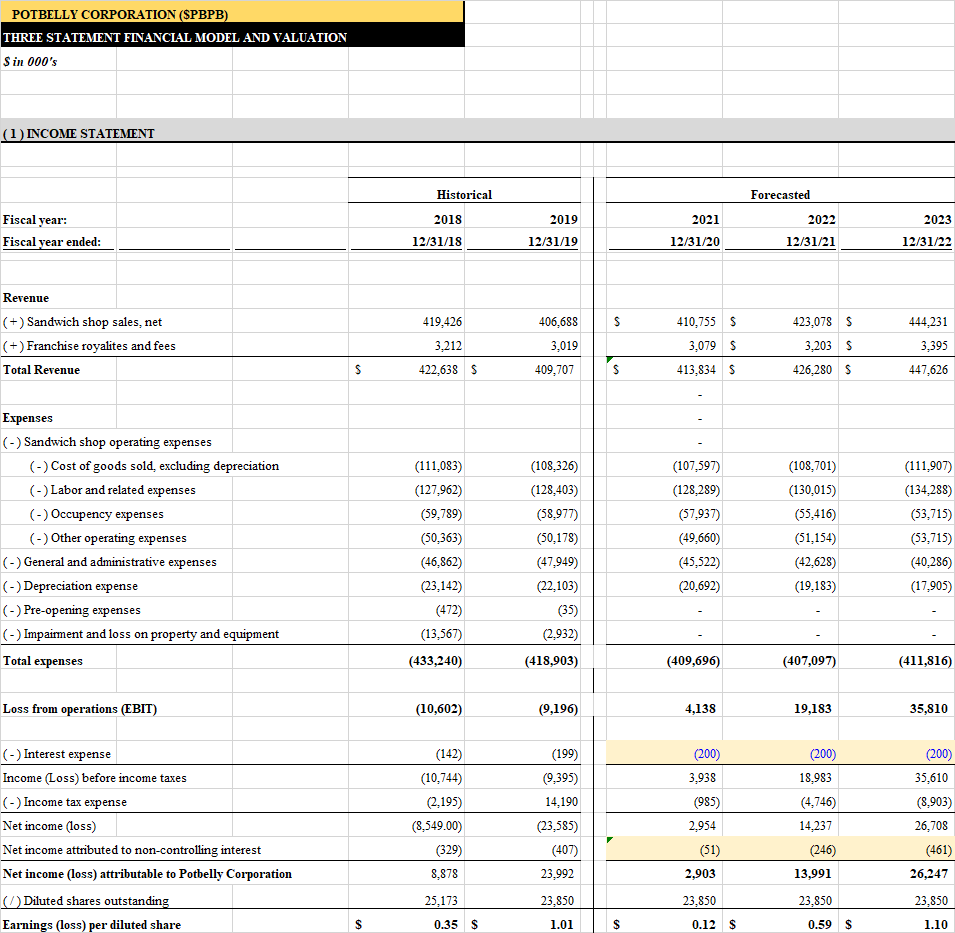
Financials & Valuation: 3 Statement Analysis
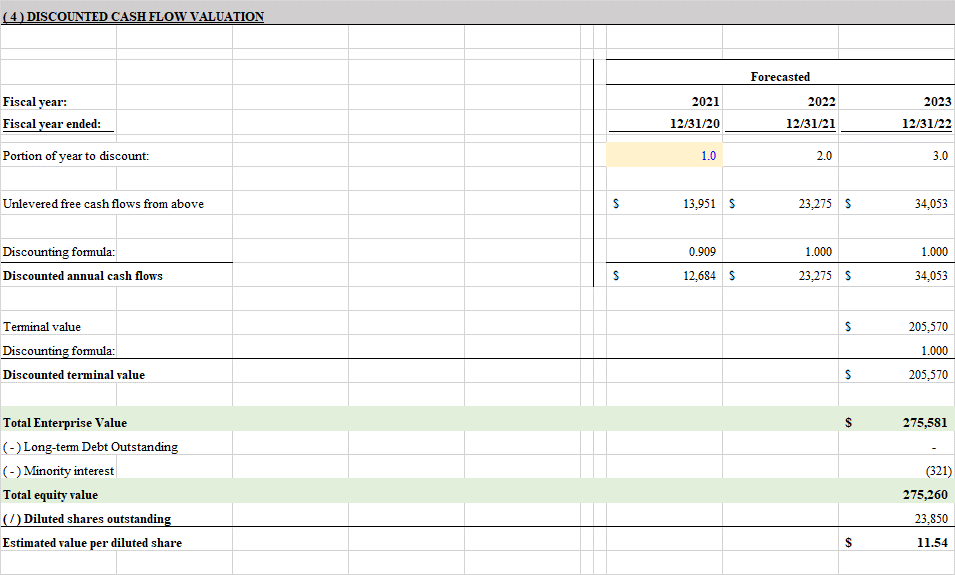
DCF
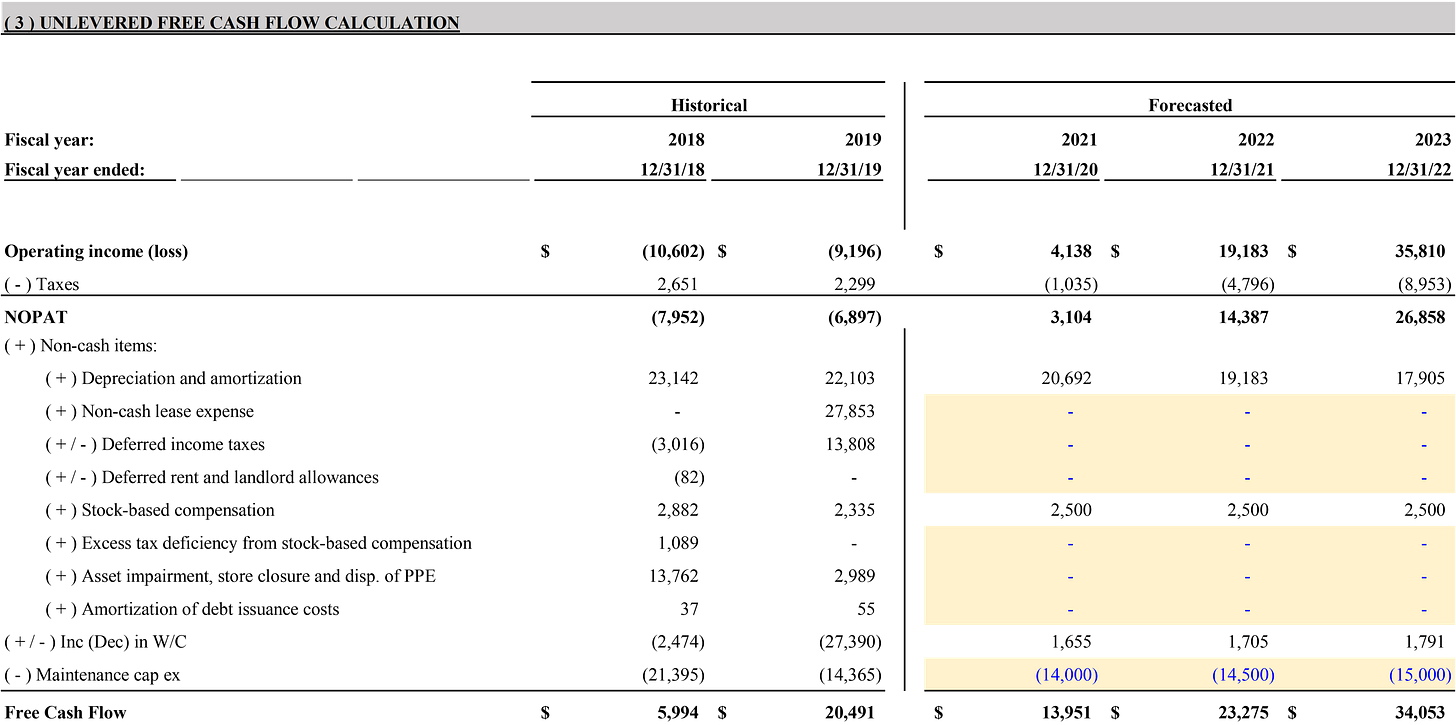
FCF Calaculations
Disclosure: I do not own any shares of $PBPB
Disclaimer: NOT FINANCIAL ADVICE. INVEST AT YOUR OWN RISK.